Why Rebooting Your Router is Important
WiFi routers are critical in managing and directing internet traffic in your network. They connect multiple devices, manage data flow, and ensure smooth communication between your devices and the internet. However, routers can experience issues that affect performance.
Common problems you can resolve by rebooting your router include: Rebooting the router may resolve these issues by:
Clearing the cache: Frees up memory and removes outdated information. Refreshing the firmware: Ensures that old firmware issues or corrupted processes are resolved. Releasing and renewing memory: Helps resolve memory leaks and other memory-related problems. Cooling down the hardware: Provides a break for the router, reducing the risk of overheating. Reorganizing the routing table: Improves the efficiency of data packet routing. Resetting DNS settings: Clears any problematic DNS entries.
Are slow internet speeds still a problem? Try restarting your phone or whatever device you’re using. This also can clear the cache and reset DNS settings.
Steps to Reboot Your WiFi Router
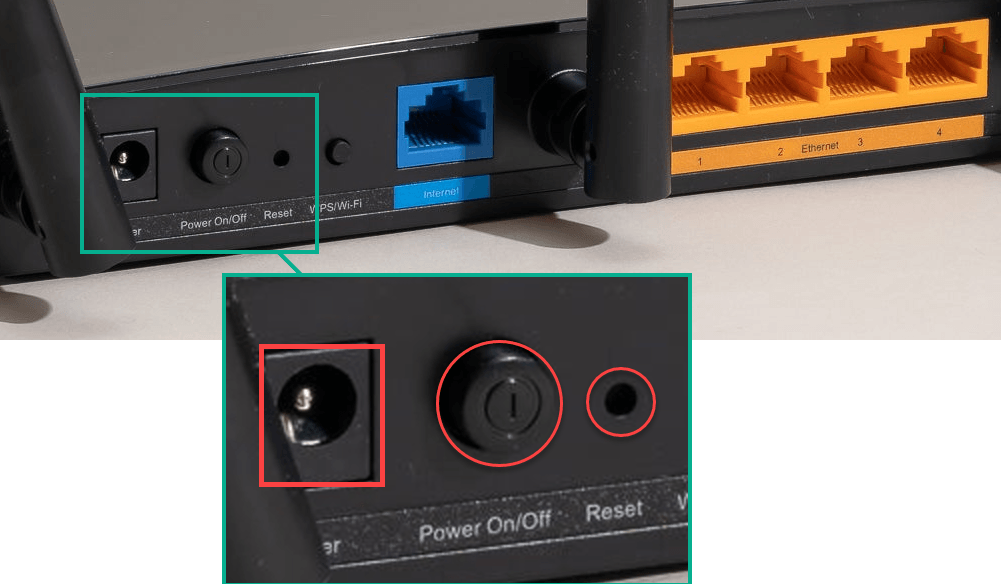
Rebooting your router is a straightforward process that involves power cycling. A hard reboot shuts down all processes and removes power from the router, whereas a soft reboot may not completely turn off power to the internal circuits. It may keep certain things running while it restarts processes and services. The two are close enough for most situations. Here’s how you can do a hard reboot: A soft reboot is similar, except you only push the power button (or sometimes a separate reset button), wait 30 seconds, and then push the power button to turn it on again. By following these steps, you should see an improvement in your network’s performance.
Router Restart vs. Router Reset
We mentioned the router reset earlier. You need to know the difference between restarting and resetting your router:
Restarting (or rebooting): This involves power cycling the router. It does not change any of your settings or configurations. Resetting: This restores the router to its factory default settings, erasing all custom configurations, such as your WiFi name and password.
Restarting is a quick fix for temporary issues, while resetting is a last resort for persistent problems. Before resetting your router, ensure you have all the necessary information to reconfigure it. Fortunately, resetting a router requires a paperclip to be stuck in the reset hole and held for at least 10 seconds. It’s not something you can do accidentally.
How Often Should You Reboot Your Router?
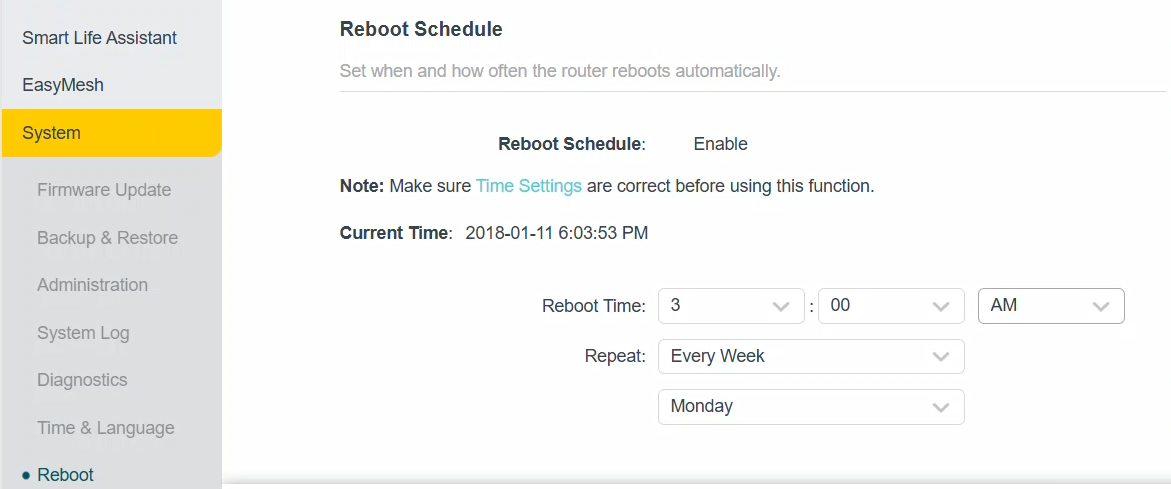
General recommendations suggest rebooting your router at least once a month to maintain performance. However, factors such as heavy internet usage, multiple connected devices, or frequent connection drops may necessitate more frequent reboots. Some manufacturers may provide specific guidelines, so it’s worth checking your router’s manual. Some routers even can schedule reboots.
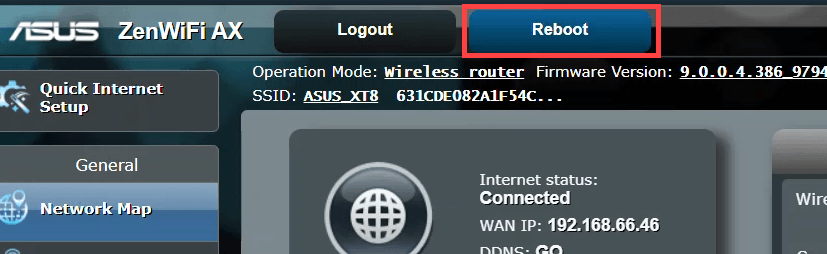
Rebooting Your Router from a PC or Mobile Device
Modern routers often come with the ability to be rebooted remotely via a web browser or mobile app. Here’s how you can do it:
Using a Web Browser
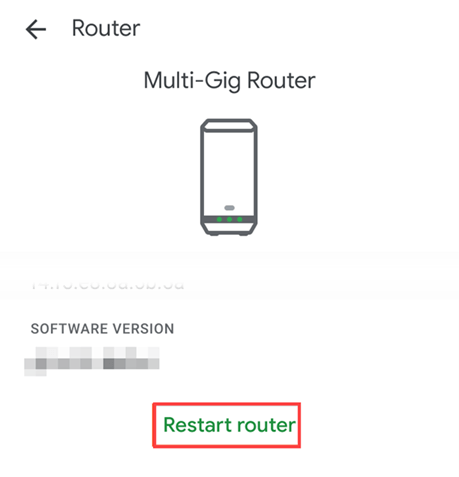
Using a Mobile App
Phone apps are convenient, especially if your router is not easily accessible. You don’t have to know the IP address of your router.
Considerations When Rebooting Your Router
When rebooting your router, keep the following in mind:
Save your work: Rebooting will temporarily disconnect your internet, so ensure any online work is saved. Check cable connections: Ensure all cables are securely connected to prevent physical damage or loose connections. Follow each cable to both ends and ensure they’re firmly seated. Understand the process: Know the difference between rebooting and resetting to avoid unintentional changes to your settings.
Conclusion
Regularly rebooting your WiFi router is a simple yet effective way to maintain a stable and efficient network. Following the steps outlined in this article, you can resolve common connectivity issues and ensure your internet performs at its best. If you encounter persistent problems, consider seeking professional assistance. Often, your internet service provider’s help desk can provide assistance, especially if it’s a router/modem device they’ve provided.